- A triangle that contains a right angle (90°or π/2 in radians) is a Right Triangle
- The right angle is denoted by a square or perpendicular symbol inside of the triangle
- The side opposite the right angle is the longest side and it is called the Hypotenuse
- The other two sides are adjacent to the right angle and are called legs
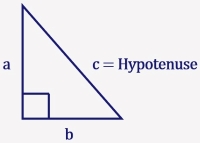
- Under the Pythagorean Theorem, the sum of the leg lengths squared is equal to the square of the length of the Hypotenuse, a2 + b2 = c2
- Under the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem, a triangle with leg lengths a, b, and c that satisfies the equation a2 + b2 = c2, is a Right Triangle
- If a, b, and c are all positive integers, then they are called a Pythagorean Triple
- Because of the 90°right angle opposite the Hypotenuse, the angles opposite the two legs are complimentary (their sum is 90°)
- If the lengths of the two legs are equal, then a 45°-45°-90° Special Right Triangle is formed
- If the Hypotenuse is twice as long as the shortest leg, or the length of the shortest leg is half of the length of the Hypotenuse, then a 30°-60°-90° Special Right Triangle is formed.
- Knowledge of the relationships between the ratios of the side lengths and the included angles is a Standard in High School Geometry under Common Core
- When those relationships are combined with such concepts as Similar Triangles, many real world problems can be solved such as the height of an object or the distance from one point to another when those measurements cannot be easily made by other means
