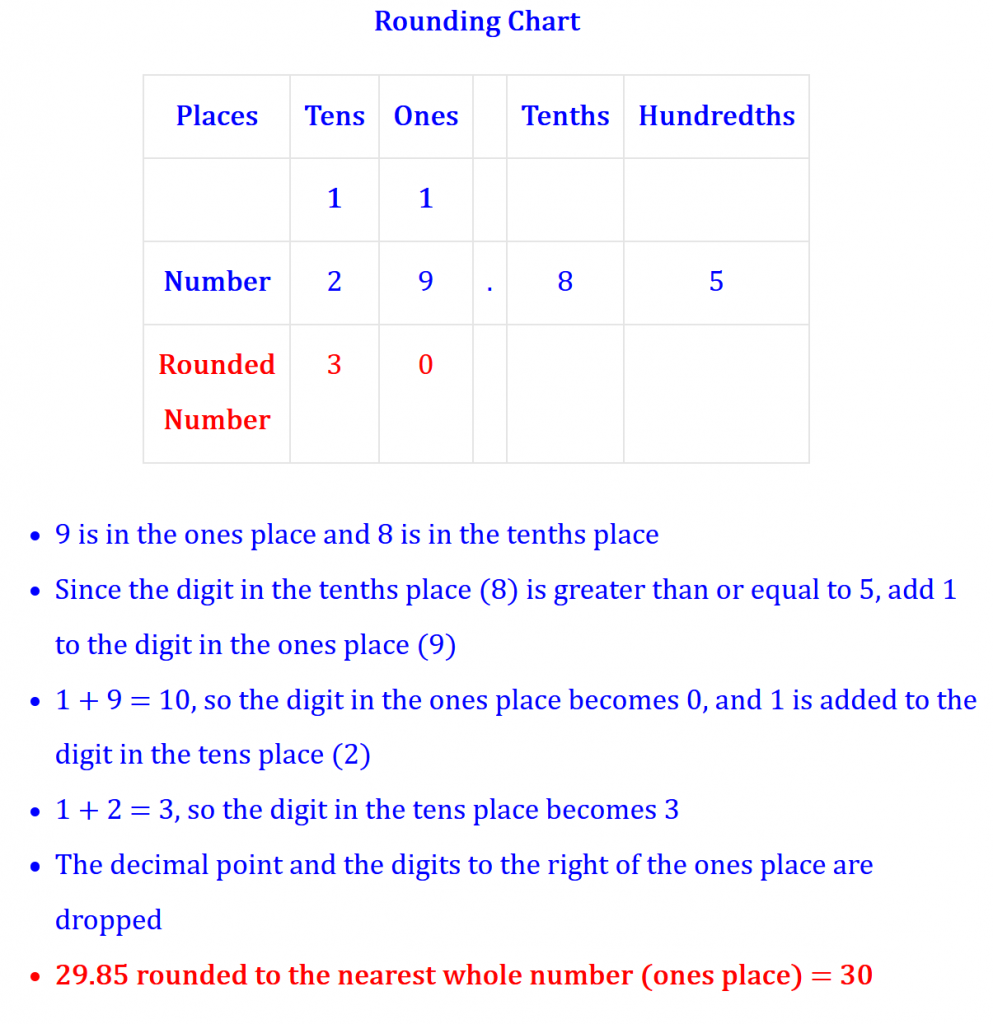
As illustrated below and by other available solutions, this application will Round a Decimal Number to the nearest Whole Number (ones place) with the aid of a rounding chart.
Students in the 5th grade should be able to round to the nearest whole number (ones place) under Common Core and Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills standards. In order to round to the nearest whole number (ones place), the digits in the ones place and tenths place must be identified. In other words, knowledge of the places digits occupy in a number is essential to the rounding process.
If the digit in the tenths place is greater than or equal to 5, then 1 is added to the digit in the ones place (rounding up). If adding 1 to the digit in the ones place results in a sum of 10, then the digit in the ones place becomes 0 in the rounded number, and 1 is added to the digit in the tens place in the number entered. Notably, this process may repeat for successive digits in places to the left of the tens place if adding 1 to the digit in the tens place results in a sum of 10.
On the other hand, if the digit occupying the tenths place in the number entered is less than 5, then the digit in the ones place does not change in the rounded number (rounding down). And the digits to the left of the ones place do not change if present. However, the decimal point and the digits to the right of the ones place are dropped in all cases.
With the intent of illustrating the step-by-step process to round a number to the nearest whole number (ones place), the application above returns a chart that puts each digit in the number entered in a row and under columns that identify the place it occupies in the number. If applicable, a 1 is placed in the column above each digit in the number entered. The application also puts the digits of the rounded number in a row under the the appropriate place columns. And finally, it returns a list that reflects the application of the steps discussed above to the number entered.
Example: 29.85